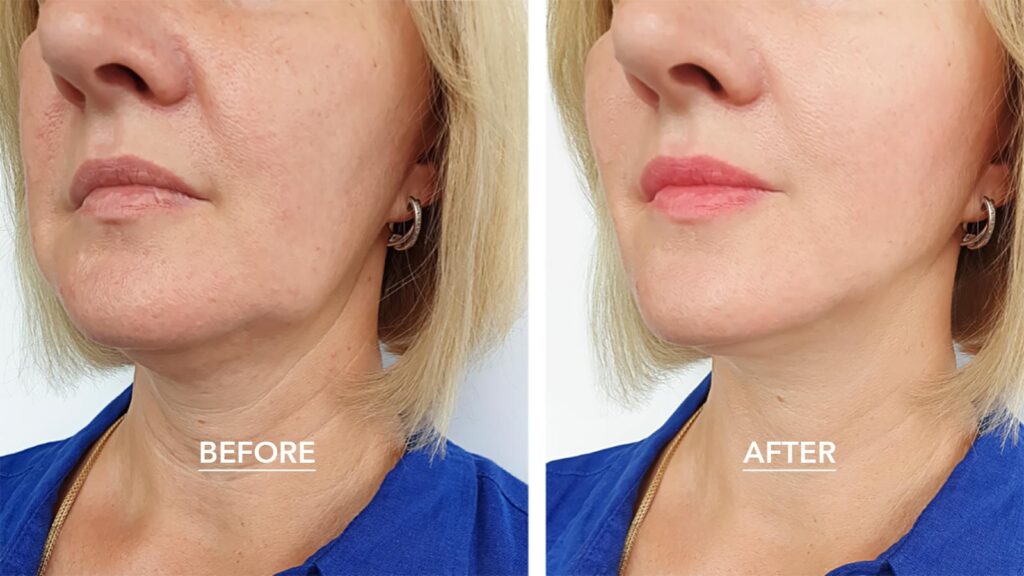
Tailored specifically for you, our compounded creams comprise of powerful ingredients to brighten your skin and reduce discolouration. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly how to use your compounded pigmentation creams for best results – from application to daily tips, ensuring you feel confident and in control of your skincare journey.
What Is In Your Compounded Creams?
Our compounded Day and Night pigmentation creams are specialised topical treatments designed to reduce hyperpigmentation, promote an even skin tone, and enhance skin texture. They contain a mix of one or more of the following active ingredients that work synergistically to address pigmentation issues at different times of the day.
Day Cream Ingredients
-
-
- Kojic Acid : A natural compound derived from fungi that acts as a skin lightener by inhibiting tyrosinase activity, reducing melanin production.
- Arbutin : A glycosylated hydroquinone that lightens skin by slowly releasing hydroquinone and inhibiting tyrosinase activity and thus inhibiting melanin production.
- Azelaic Acid : Reduces melanin synthesis and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Hyaluronic Acid : Hydrates and plumps the skin, aiding other active ingredients.
- Mandelic Acid : Exfoliates and promotes cell turnover to help fade pigmentation.
- Kaolin : Absorbs excess oil and impurities.
- Marine Collagen : Improves skin elasticity and hydration.
- Ceramides : Restores the skin barrier and retains moisture.
-
Night Cream Ingredients
-
-
- Hydroquinone : A skin-lightening agent that reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is crucial in melanin production. Reduces melanin production.
- Tretinoin : A derivative of Vitamin A, commonly used to treat acne and reduce the appearance of fine lines and hyperpigmentation. Enhances skin cell turnover and collagen production.
- Triamcinolone & Fluocinolone : A corticosteroid used to reduce inflammation and redness associated with skin conditions
- Tranexamic Acid : Primarily used to treat melasma and hyperpigmentation by inhibiting the interaction of melanocytes with keratinocytes and reducing melanin synthesis.
- AHAs (Lactic, Glycolic) : Includes ingredients like Lactic and Glycolic Acid, which exfoliate the upper layer of skin and promote cell turnover, aiding in improving skin texture, tone and reducing dark spots.
- BHAs (Salicylic Acid) : Primarily Salicylic Acid, an oil-soluble exfoliant that penetrates into pores, making it effective for acne. Exfoliate inside the pores and improve skin texture.
-
How Do These Ingredients Collectively Work?
-
-
- Tyrosinase Inhibition : Hydroquinone, Kojic Acid, and Arbutin inhibit tyrosinase, a vital enzyme in melanin production. By blocking this enzyme, they reduce pigmentation.
-
-
-
- Gradient of Exfoliation : AHAs and BHAs help in exfoliating the skin’s outer layer, increasing turnover, and promoting smoother, brighter skin.
-
-
-
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties : Triamcinolone and Azelaic acid reduce inflammation, helping to calm irritated skin and enhance the efficacy of other ingredients.
-
Combined Use in Melasma Treatment
-
-
- Synergistic Effects : When used together, these compounds can have a synergistic effect. For example, Hydroquinone or Arbutin may inhibit melanin production, while Tretinoin enhances the turnover of pigmented skin cells, thus leading to faster and more effective depigmentation.
- Increased Efficacy : Using these agents in combination can target different pathways involved in melasma, enhancing overall treatment effectiveness and improving skin texture.
-
How To Apply Your Creams
Morning Application (Day Cream)
-
-
- Cleanse : Start with a gentle facial cleanser.
- Tone (optional) : Use a toner to balance your skin.
- Apply Day Cream : Use a pea-sized amount, usually ONE pump, evenly to the face, avoiding the eye area.
- Moisturise (optional) : Follow with a lightweight moisturiser such as our compounded moisturiser (Link)
- Sun Protection : Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) as the final step.
-
Evening Application (Night Cream)
-
-
- Cleanse : Cleanse your face thoroughly.
- Tone (optional) : Use a toner if preferred.
- Apply Night Cream : Apply a small amount, usually ONE pump, to your face, avoiding the eye area. Use every alternate night for the first 2 weeks and increase frequency gradually. (See below)
- Moisturise (optional) : Follow with a lightweight moisturiser such as our compounded moisturiser (Link)
-
Increase Frequency Gradually:
-
-
- Week 2 and Beyond : If no significant irritation occurs, gradually increase to every weekday night during the third week.
- By Week 4 : If your skin tolerates the cream well, you can begin using it every night. If you experience irritation at any point, revert to the previous frequency.
-
Moisturiser:
-
-
- Hydration : After applying the compounded cream, wait about 5-10 minutes, then apply a gentle moisturiser if needed to minimise dryness and irritation.
- Moisturiser Type : Choose a fragrance-free and non-comedogenic moisturiser for your skin type.
-
Sun Protection:
-
-
- Daily Sunscreen : Use a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher sunscreen every morning. Apply generously even on cloudy days, as both Tretinoin and Hydroquinone can make your skin more sensitive to UV rays.
- Reapplication : Reapply sunscreen every two hours if you’re outdoors, and consider wearing hats or sunglasses for additional protection.
-
When Will I Start Seeing Results?
-
-
- Duration of Use : For optimal results, use both creams consistently for 12 weeks or as directed by a healthcare provider. Expect to follow a prescribed regimen long-term for maintenance.
- When to Start Seeing Effects : Improvements in skin tone and texture may be visible within 4 to 12 weeks , (4 weeks is an average skin cell turnover time) with full results potentially taking several months depending on individual skin response.
-
Will I Experience Any Side Effects?
While many users tolerate these creams well, possible side effects can include:
-
-
- Redness : Slight irritation or redness may occur, especially with initial use.
- Dryness/Peeling : Common with tretinoin and AHAs due to their exfoliating properties.
- Sensitivity : Increased sensitivity to sunlight; therefore, diligent sun protection is essential.
- Allergic Reactions : In rare cases, some individuals may experience allergic reactions leading to itching or swelling.
- Signs to Watch : Look for redness, peeling, flaking, or irritation. Some initial mild irritation can be normal, but severe reactions warrant discontinuation.
-
If any severe side effects or allergic reactions occur, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Follow-up :
-
-
- Regular Appointments : Schedule follow-ups every 6-8 weeks or as recommended to assess the effectiveness of the cream.
- Adjustments : Your pharmacist or doctor may adjust the formulation, change the frequency, or suggest additional treatments based on your skin’s response.
-
How Do I Store My Creams?
-
-
- Temperature : Store the cream in a cool, dry place away from light and moisture, as heat can degrade active ingredients.
- Container : Keep the product tightly closed to prevent contamination. You can choose to refrigerate your products. Do not freeze
- Duration : Check the expiration date on the packaging, and do not use past this date or if the product appears discolored or has changed in consistency. Compounded creams can be kept in room temperature for 3 months and in the fridge for up to 6 months.
-
Want to start your pigment-free journey? Purchase our Pigmentation Transformation Package.
Ready to transform your skincare routine? Book a skincare consultation with us today!
Follow us on Instagram for the latest skincare tips and trends!
Frequently Asked Questions
Below we have answered some common questions around how to use your compounded pigmentation creams, what to expect and mistakes to avoid. If you can’t find the answer you are looking for, don’t hesitate to contact us.
Can I use both creams simultaneously?
Yes, but they should be applied at their respective times—day cream in the morning and night cream in the evening.
Is sunscreen still necessary during treatment?
Yes, sunscreen is crucial, especially during the day when using pigmentation treatments, as they can increase your skin’s sensitivity to UV rays. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your skin from sun damage and prevent further pigmentation.
What should I do if I miss an application?
If you miss an application, use the cream as soon as you remember. If it is close to the time for your next application, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular schedule. Do not apply double the amount to make up for the missed dose.
Can I use makeup while using these creams?
Yes, you can use makeup after applying your day cream or night cream. Allow approximately 10-15 minutes for the creams to absorb into your skin before applying makeup.
Can I combine these creams with other skincare products?
Be cautious when combining these creams with other active ingredients. Avoid using other strong exfoliants or potent actives on the same day, as this can increase the risk of irritation. Consult your dermatologist for personalised advice based on your skin type and treatments.
Are there specific skin types that should avoid these creams?
Individuals with very sensitive skin, active eczema, or severe rosacea should consult their healthcare provider before using these creams. Your healthcare provider can recommend alternative treatments that are more suitable for your skin type.
Is it okay to use these creams while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new skincare treatments during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as some ingredients may not be advisable for use in these circumstances.
What is compounded melasma cream?
Answer: Compounded melasma cream is a custom-formulated topical medication made by a pharmacist to address specific skin concerns related to pigmentation disorders like melasma. These creams often combine active ingredients like hydroquinone, tretinoin, kojic acid, and corticosteroids to help lighten dark patches and improve skin tone.
How does compounded cream work for pigmentation?
Answer: Compounded creams work by targeting the pathways involved in melanin production. Ingredients like hydroquinone inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, which is crucial for melanin synthesis, while tretinoin promotes skin cell turnover, helping to shed pigmented skin cells faster. This combination can effectively reduce the appearance of dark spots and improve overall skin tone.
How long does it take for compounded cream to work on melasma?
Answer: Results can typically be seen within 4 to 12 weeks of consistent use, but this varies based on individual skin types, the specific formulation used, and adherence to treatment protocols. It’s essential to remain patient and maintain regular follow-ups with a dermatologist.
Can I use compounded cream during pregnancy?
Answer: Pregnant or nursing individuals should consult their healthcare provider before using compounded creams for pigmentation. Some ingredients, particularly tretinoin and hydroquinone, may not be recommended during pregnancy due to potential risks.
What are the side effects of using compounded pigmentation creams?
Answer: Common side effects may include redness, irritation, dryness, peeling, and increased sun sensitivity. If severe reactions or persistent irritation occur, it is essential to contact your dermatologist for guidance.
Can I use sunscreen while using melasma cream?
Answer: Yes, daily use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) is crucial. Compounded pigmentation creams can increase sun sensitivity, making sun protection vital to prevent worsening pigmentation and protect sensitive skin.
How should compounded creams be stored?
Answer: Store compounded creams at room temperature in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Proper storage is crucial to maintain the efficacy of the active ingredients.
Can I use other skincare products with compounded pigmentation creams?
Answer: It is generally best to avoid using products with active ingredients (like retinoids, AHAs, or BHAs) or strong exfoliants simultaneously with compounded pigmentation creams unless directed by a dermatologist. This helps prevent excessive irritation. Always consult your dermatologist for personalised advice on compatible products.
How do I know if the compounded cream is working?
Answer: You may notice gradual lightening of dark spots and an improvement in skin tone over several weeks. Keeping a journal of your skin’s progress and checking in with your dermatologist during follow-ups can help assess effectiveness.
Is compounded cream covered by insurance?
Answer: Coverage for compounded creams can vary based on your insurance plan. It’s best to contact your insurance provider or discuss with your pharmacist to determine if your specific compounded cream is covered.
These questions and answers can help provide clarity and guidance to individuals considering or currently using compounded prescription creams for pigmentation and melasma.
References
-
-
- Brenner, M., et al. (2009). “The Role of Alpha-Hydroxy Acids in the Treatment of Hyperpigmentation.” Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology .
- Draelos, Z. D. (2010). “Cosmetic Dermatology: Products and Procedures.” Wiley-Blackwell .
- Gupta, A., et al. (2014). “Kojic Acid: A Review of its Applications in Cosmetic Products.” Clinical Cosmetic Investigational Dermatology .
- Halpern, J. (2016). “Topical Agents for Hyperpigmentation.” Dermatologic Therapy .
- Kanan, H. (2010). “Pharmacologic Approaches to the Treatment of Hyperpigmentation.” Dermatologic Clinics .
- Kumar, R., & et al. (2018). Tretinoin and its role in skin management. Dermatological Therapy .
- Kumar, D., & et al. (2019). Hydroquinone in skin hyperpigmentation
-

Lane Khin, the compounding pharmacist of My Skin Pharmacy, brings a wealth of knowledge from the worlds of pharmacy and dermatology to the table. With degrees in Pharmacy and Applied Science from QUT, Lane combines a deep understanding of compounding and skincare with a friendly, accessible approach. Through My Skin Magazine, Lane shares her expertise, offering readers practical advice and insights into personalised skincare solutions. Lane has a real passion for helping others achieve their best skin.